A view from space
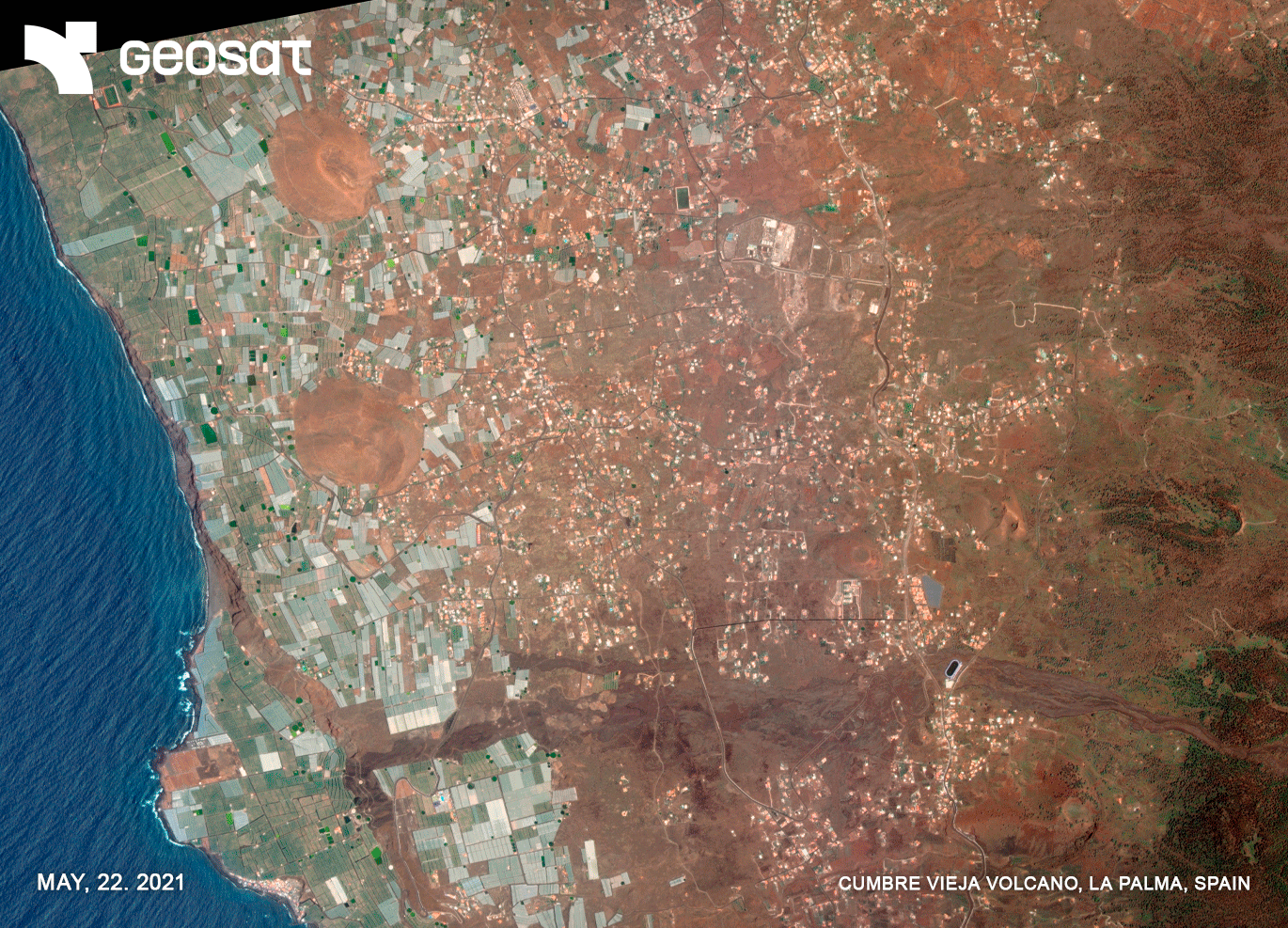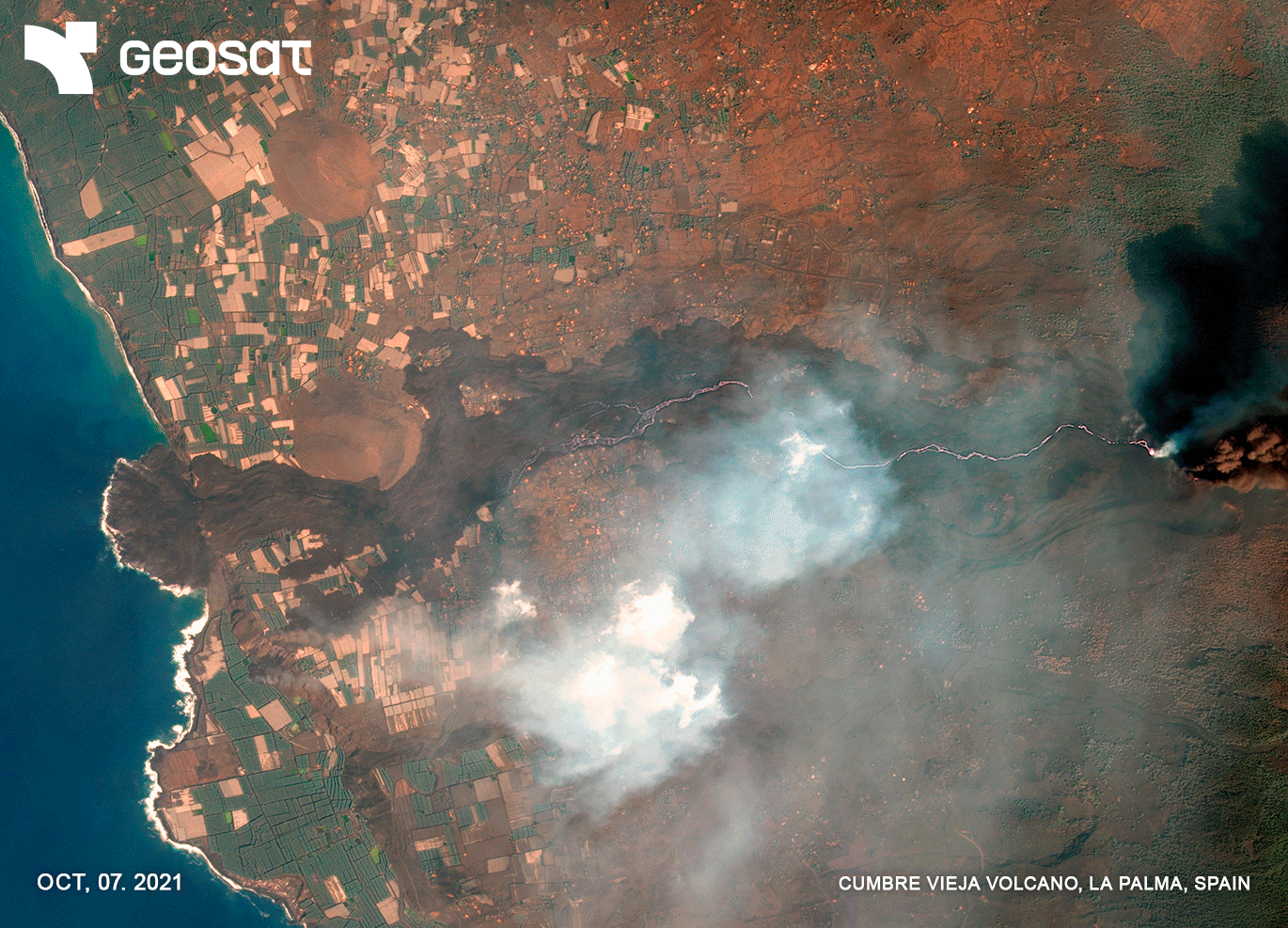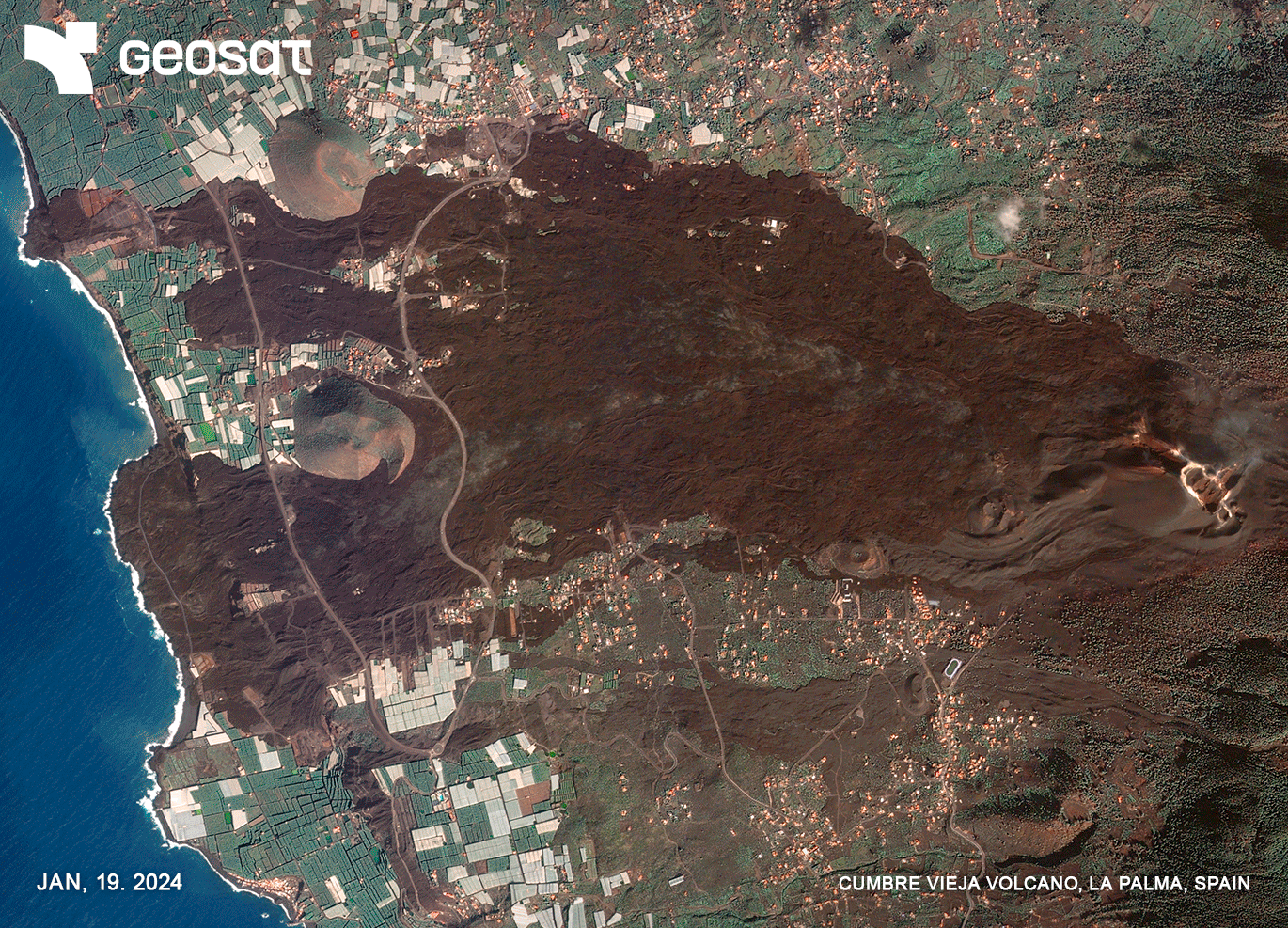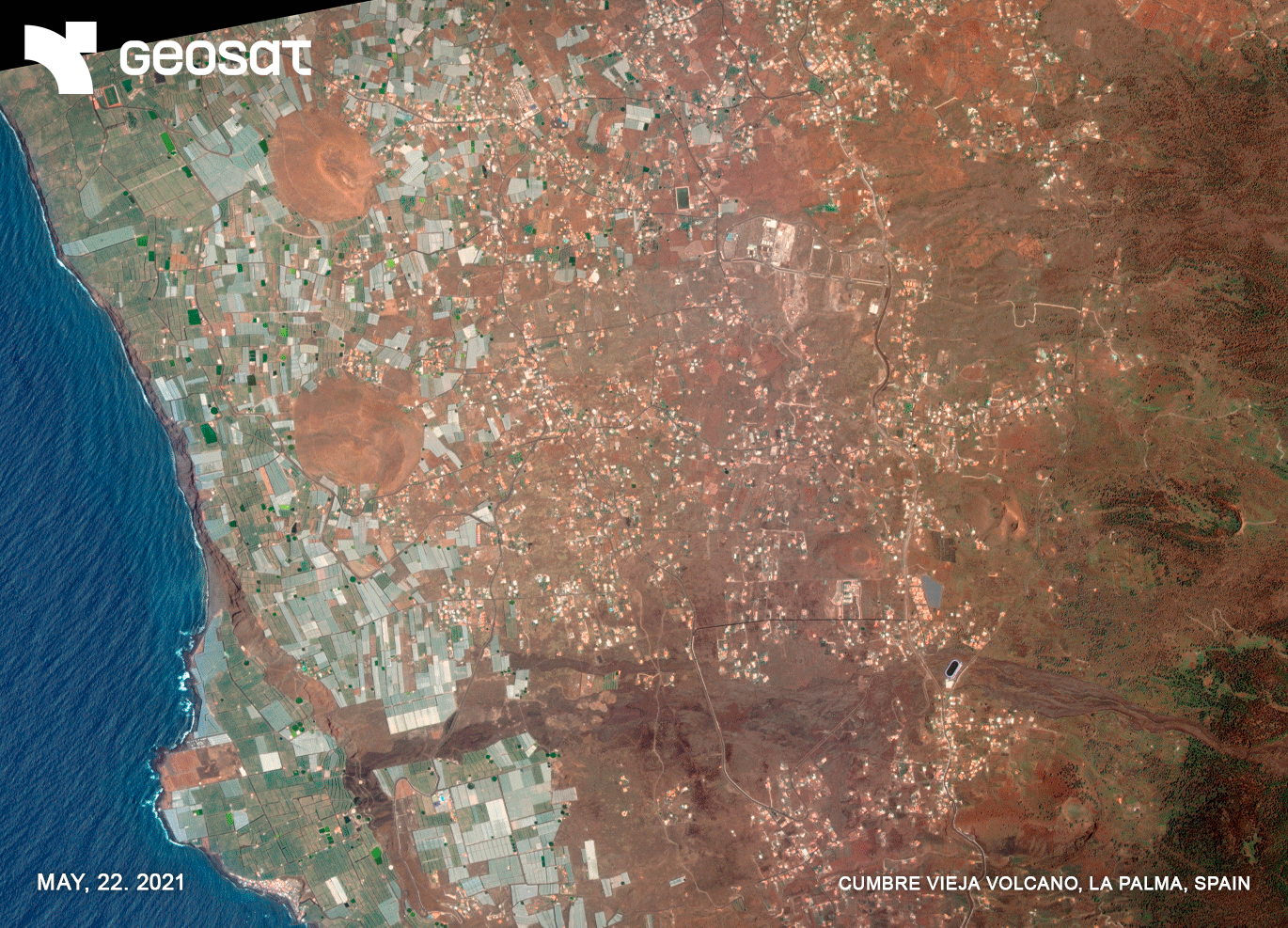
On September 19, 2021, the volcanic eruption began in the Montaña Rajada area on La Palma Island. After 85 days, the lava flows spread and reached the coast. In its path, it destroyed buildings, houses, agricultural plantations, factories and industrial warehouses, leisure and hotel businesses, schools, temples, parks and squares, making them disappear or rendering them unusable. The ground and each of the plots of land were invaded by the lava flow that, like a great mantle, made them disappear. More than 7000 people were evacuated.
GEOSAT’s satellite images offered a comprehensive view of the island from space and helped public administrations to provide an immediate response to the emergency crisis, preventing damage to people, guaranteeing their safety and trying to reduce damage to property and land.
GEOSAT’s damage analysis through Artificial Intelligence (AI)
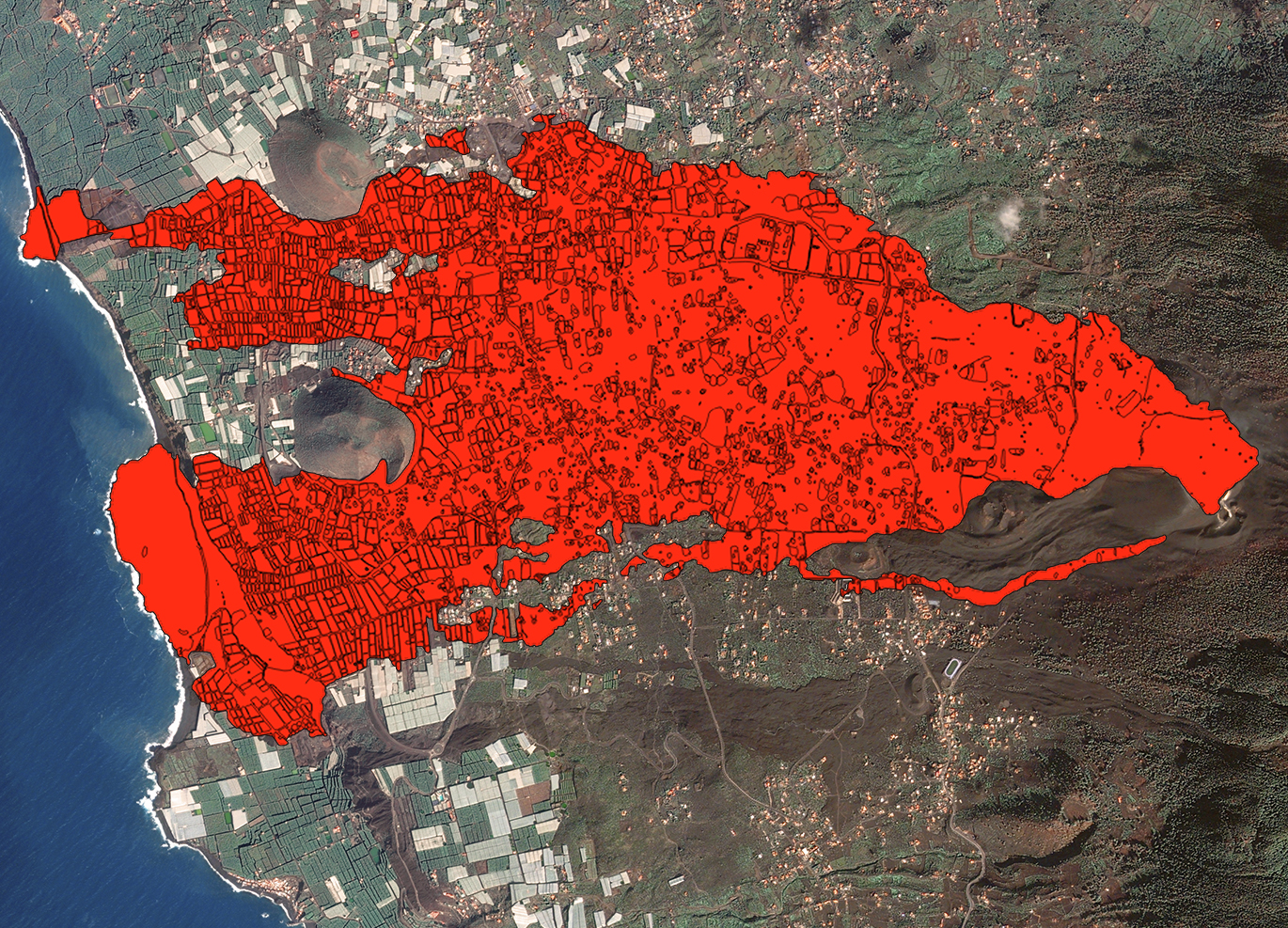
GEOSAT utilizes AI and Machine Learning to enhance its remote sensing and satellite imagery analysis capabilities. GEOSAT can efficiently process vast amounts of visual data, automatically identifying and segmenting various geographic and environmental features. The use of this data is particularly useful in monitoring natural disasters, such as the Cumbre Vieja eruption, where precise and timely analysis of affected areas is critical.
GEOSAT’s ability to quickly and accurately delineate volcanic activity, lava flows, and impacted zones, allowed GEOSAT to provide detailed and actionable insights, aiding in disaster response and recovery efforts of the island.
It is estimated that the volcano expelled 159 million cubic meters of lava, which covered more than 1,219 hectares of land (equivalent to 1,707 soccer fields), buried 73.8 kilometers of roads and affected 2,988 buildings. Within the agricultural sector, the lava razed 370 hectares of plantations.
The recovery of normality, as far as the agricultural perspective is concerned, covers an area of about 700 hectares of the +1,200 hectares affected by the lava flow.
The advantages offered by GEOSAT & the path to recovery
GEOSAT’s analytics, based on AI, in the volcanic eruption recovery process showed numerous advantages, including:
- Rapid Damage Assessment: GEOSAT quickly segmented and identified areas affected by the eruption, such us lava flows, ash deposits and destroyed infrastructure allowing authorities to prioritize areas for immediate intervention and resource allocation.
- Accurate Mapping: With its high precision in delineating contours and boundaries, GEOSAT’s analytics provided detailed and accurate maps of the affected regions. These maps were crucial for planning reconstruction efforts.
- Efficient Resource Management: By segmenting and analyzing the impacted areas, GEOSAT helped in identifying the extent of damage to natural resources, agricultural lands, and water bodies. This information aids in effective resource management and restoration planning.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: The continuous monitoring of the affected areas, allowed GEOSAT for the tracking of changes over time. This capability was essential for understanding the long-term impacts of the eruption and for evaluating the effectiveness of recovery efforts.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: The detailed data and insights provided by GEOSAT supported better decision-making by authorities and stakeholders. It facilitated evidence-based strategies for rebuilding infrastructure, restoring ecosystems, and ensuring community resilience.
- Automated Analysis: GEOSAT automated the segmentation process, significantly reducing the time and effort required for manual analysis. This automation accelerated the overall recovery process, allowing teams to focus on critical tasks.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: GEOSAT assessed the environmental impact of the eruption by segmenting affected ecosystems and habitats. This information was crucial for developing strategies to mitigate environmental damage and promote ecological recovery.
Overall, the usage of GEOSAT’s satellite data together with AI analytics in the recovery process of volcanic eruptions like Cumbre Vieja enhances the efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness of response and rehabilitation efforts, ultimately contributing to quicker and more smooth recovery.
Thanks to our own satellites, together with our partners, we deliver high quality imagery and analytics for high impact insights which result in improved decision making.