The A-5 Undergrounding Project Reconnecting Madrid’s Southwest
The undergrounding of the A-5 highway is one of Madrid’s most ambitious urban infrastructure projects in recent decades. The intervention focuses on a 3.2 km urban section of a major roadway that has historically acted as a physical and visual barrier between neighborhoods in the southwest of the city.
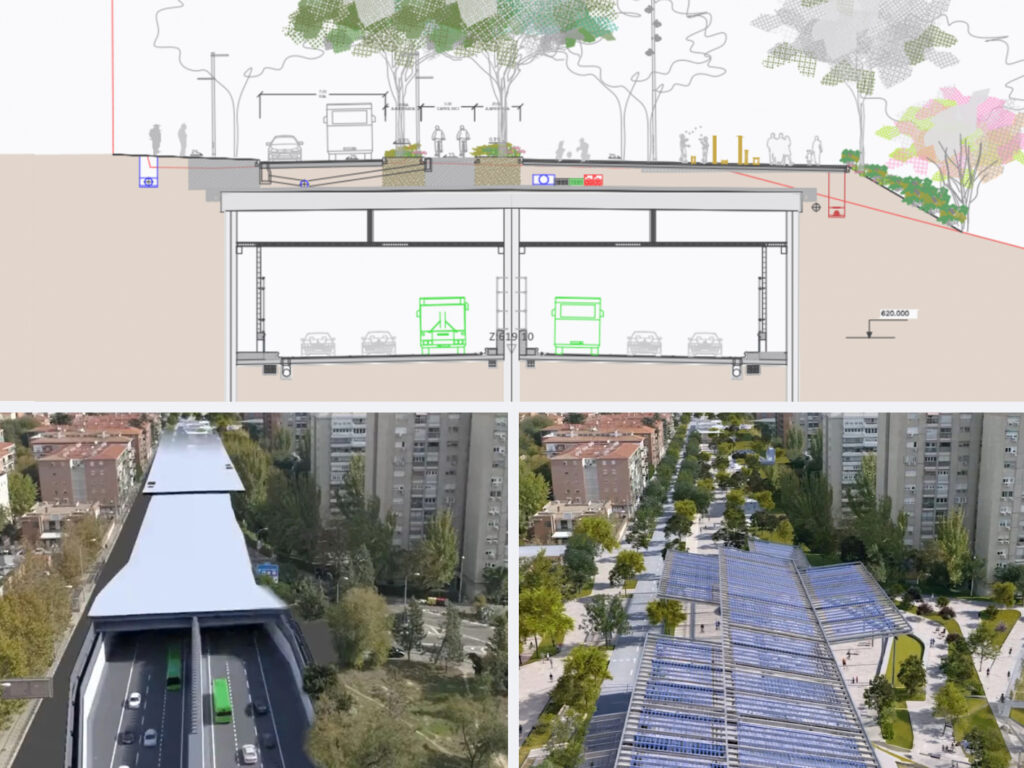
Beyond increasing road capacity, the project seeks to redefine the role of the A-5 within the urban fabric. By relocating traffic underground, the long-term objective is to recover surface space for public use, improve connectivity between neighborhoods, and enable the creation of a future green corridor prioritizing pedestrians, cyclists, and urban life.
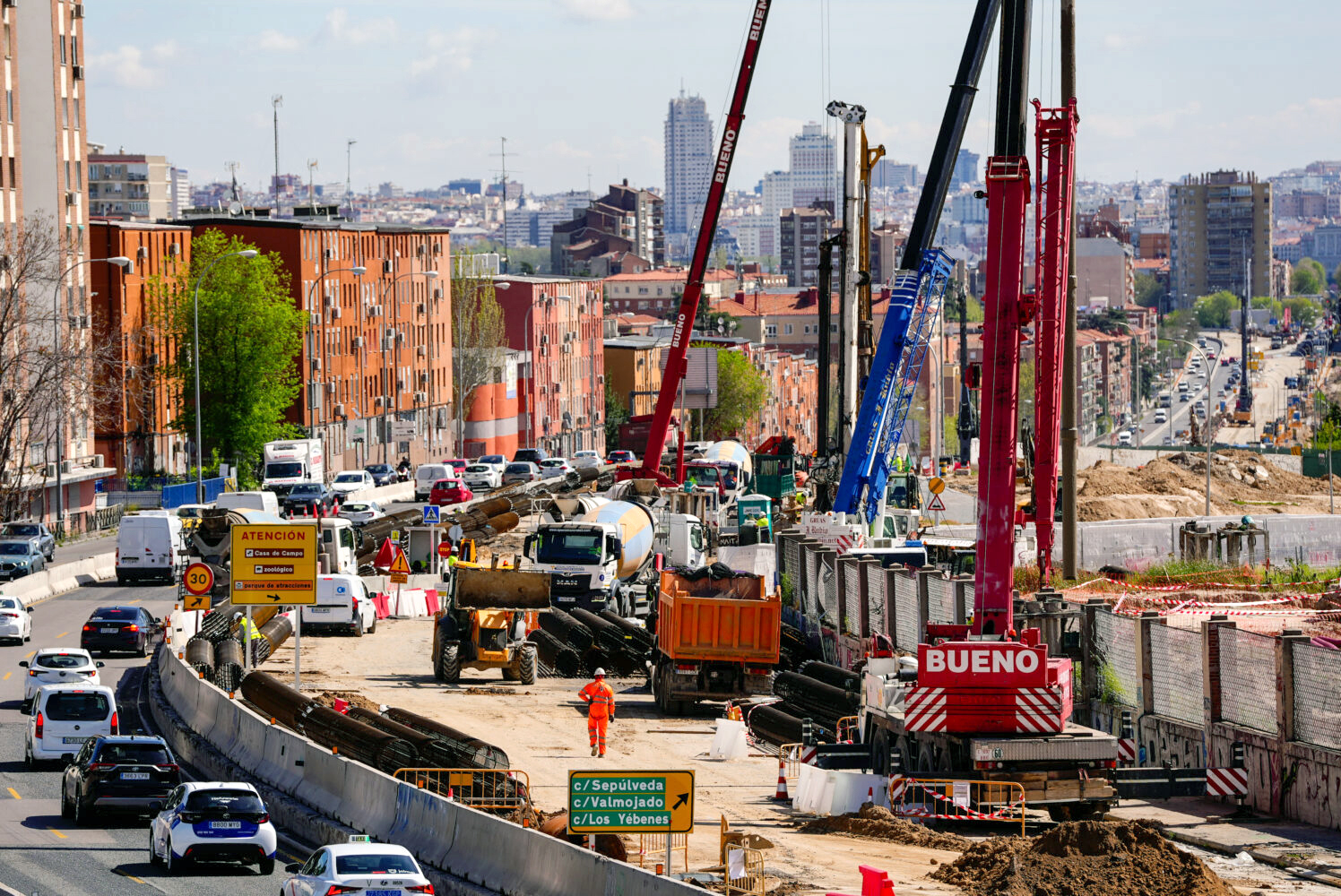
During construction, traffic continues to operate at the surface through temporary lane diversions, allowing tunnel excavation and structural works to progress. This makes the A-5 undergrounding a particularly interesting case; a large-scale infrastructure project evolving dynamically within a dense urban environment.
Observing Change from Space, Before and During Construction
Earth Observation (EO) offers a unique perspective for understanding how complex infrastructure projects evolve over time. In the case of the A-5 undergrounding, satellite imagery clearly captures the transition from a fully operational urban highway to an active construction corridor.
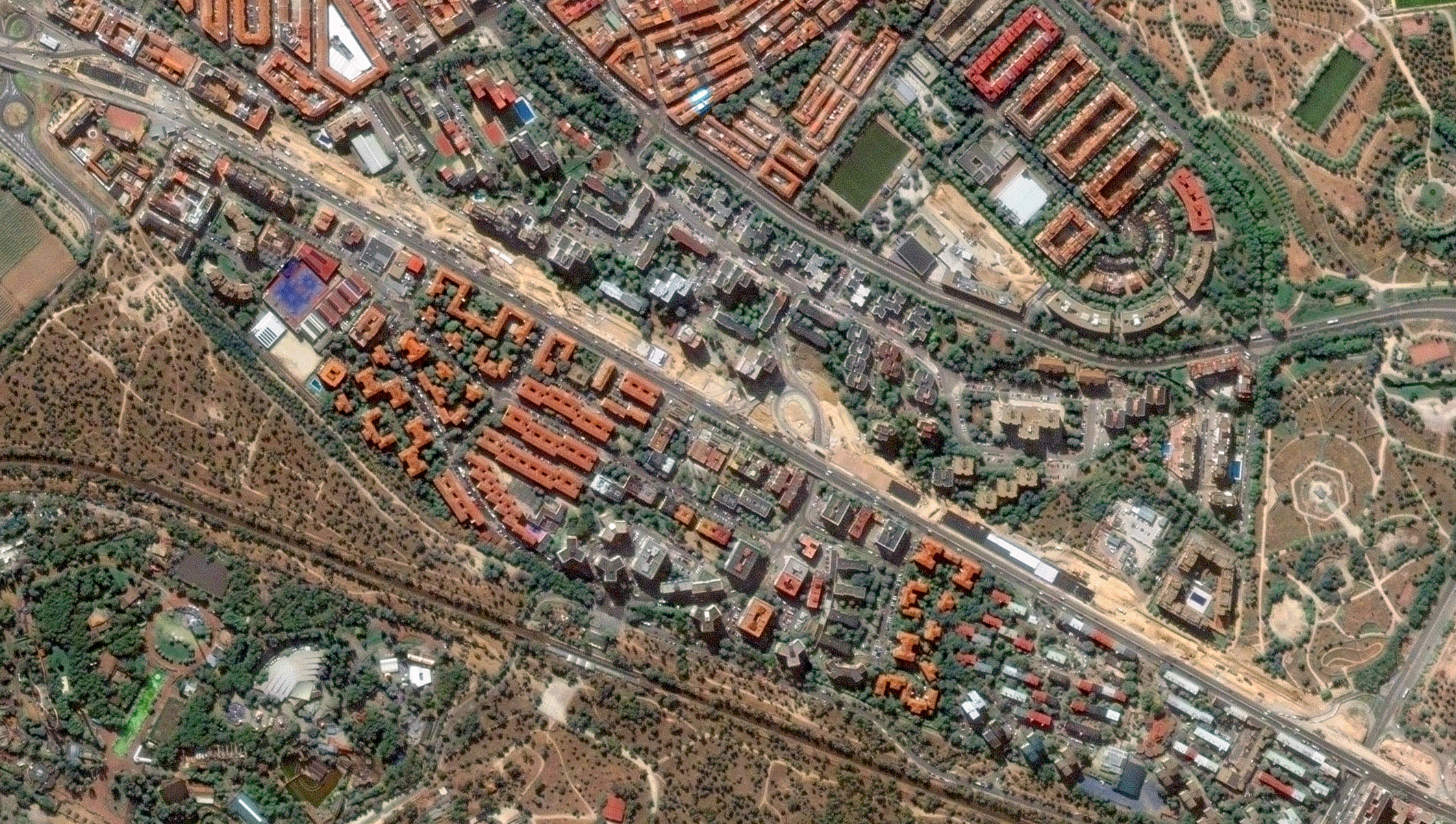
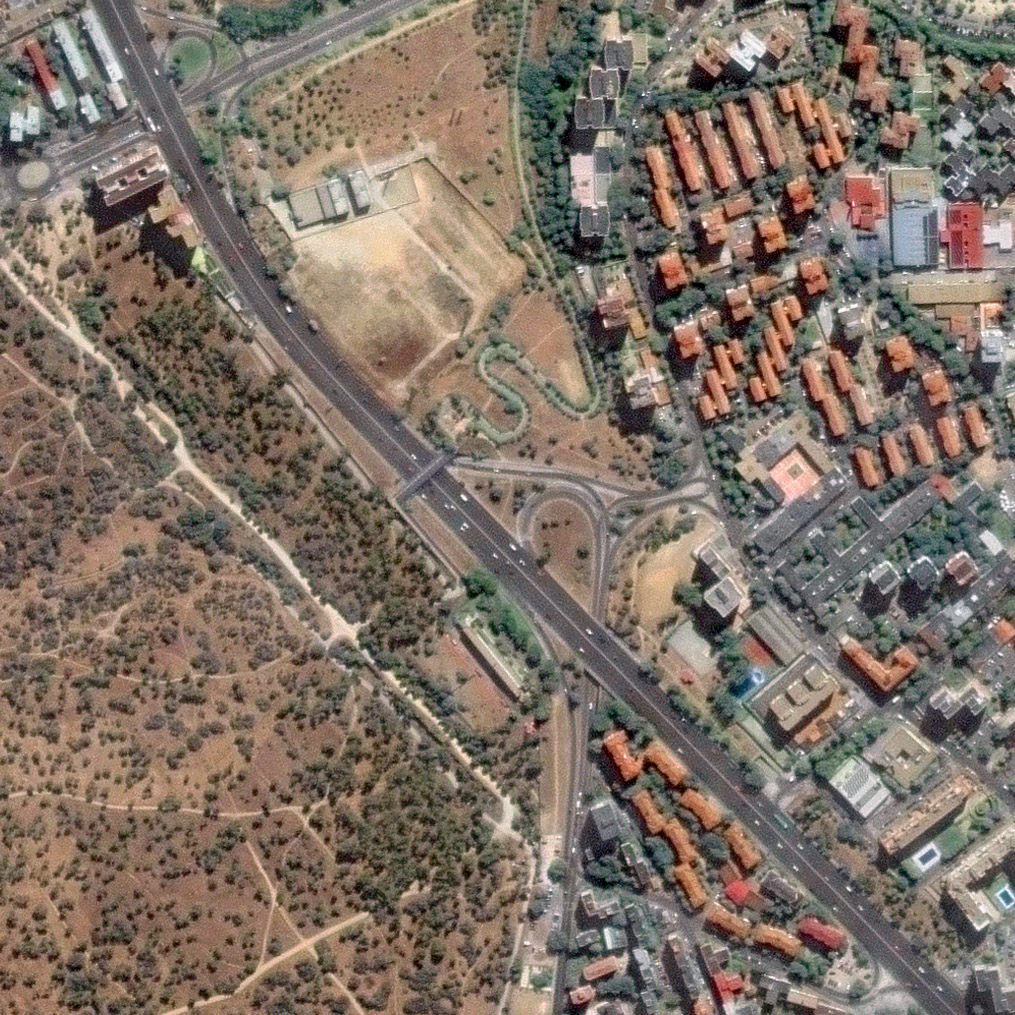
Before construction. Satellite imagery from 2024 shows the A-5 as a continuous surface highway, with traffic lanes occupying most of the available space. From above, the road reads as a clear linear barrier, limiting transversal connectivity between adjacent neighborhoods. Traffic patterns are stable, and the surrounding urban fabric shows minimal interaction across the corridor. This image provides a critical baseline reference, capturing land use, traffic layout, and the spatial relationship between the highway and its surroundings prior to construction.
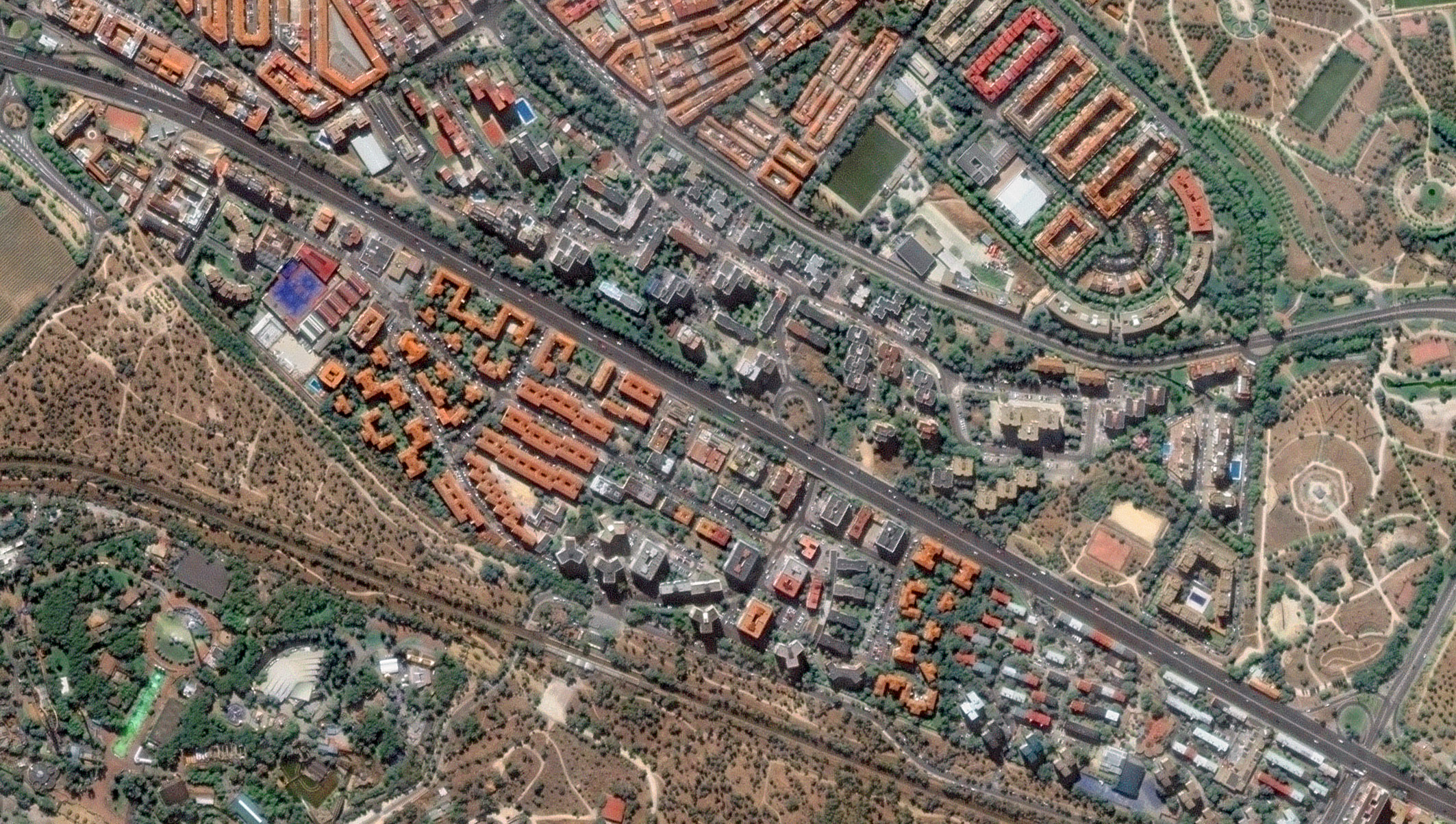
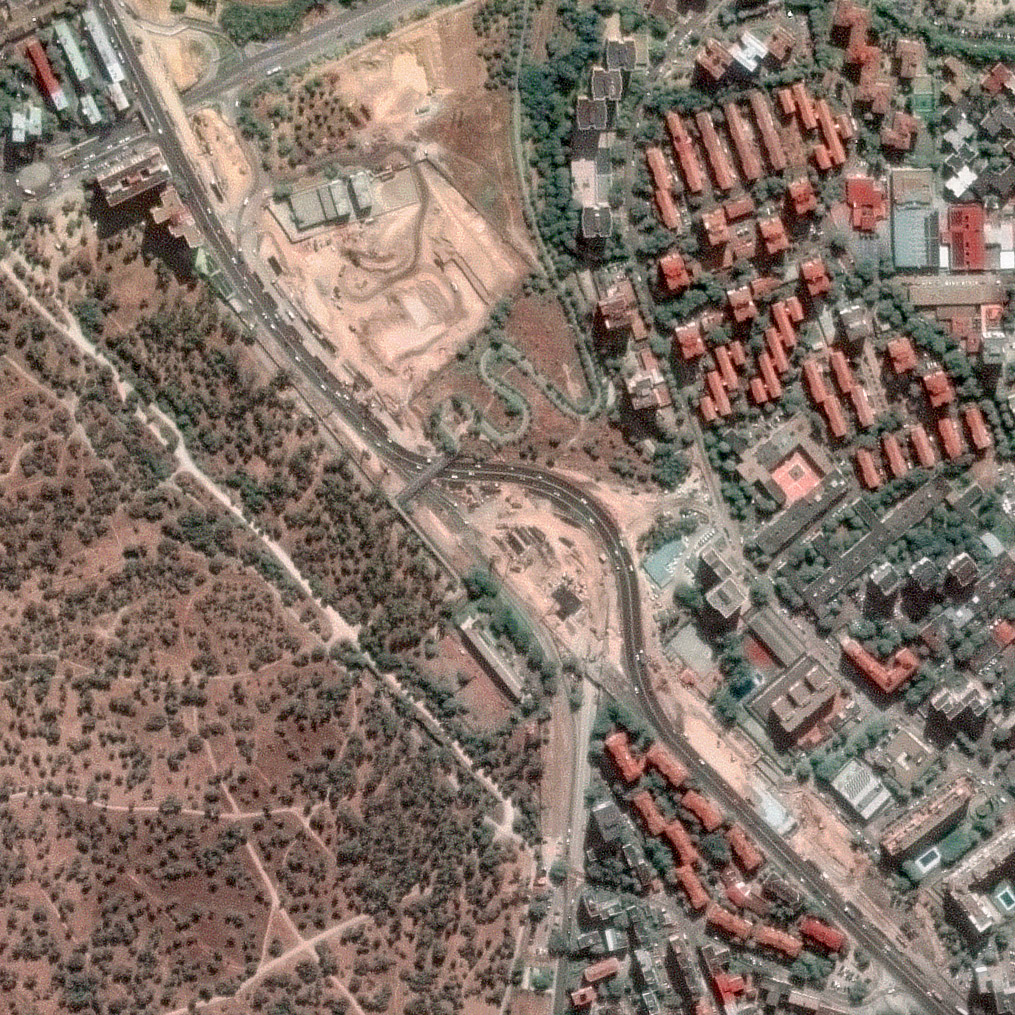
During construction. By 2025, the satellite view reveals a markedly different configuration. While traffic still runs at the surface, temporary lane realignments are clearly visible, alongside extensive construction footprints, excavation zones, and logistical areas supporting tunnel works. From space, it becomes possible to identify; Shifts in traffic alignment, Active construction areas along the 3.2 km stretch, and progressive occupation of surface space by works infrastructure.
Although traffic has not yet been relocated underground, the imagery already reflects a city in transition, where mobility is being temporarily reorganized to enable long-term structural change. Without requiring ground access, satellite data allows teams to visually document progress, assess temporary traffic solutions, and track the spatial impact of construction activities over time.
Earth Observation key tool for Monitor Infrastructure Works
Large urban infrastructure projects generate continuous change across wide areas and extended timelines. EO complements traditional on-site methods by providing consistent, scalable, and objective data from space.
- Reduced Need for On-Site Visits. While in-situ inspections remain essential, satellite imagery significantly reduces the need for frequent physical visits along the entire corridor. A single image can cover in Very High Resolution the full project extent, minimizing travel costs, reducing exposure to active construction zones, and allowing experts to focus on targeted site visits where they add the most value.
- Independent, Objective, and Scalable Data. Satellite imagery provides a consistent and independent data source, acquired using the same geometry and methodology over time. This ensures that observed changes reflect real-world evolution rather than differences in data collection, enabling reliable comparisons across months or years.
- Near Real-Time Image Deliveries. A key advantage of satellite imagery is the availability of NRT image deliveries, providing updated views shortly after acquisition. For projects like the A-5 undergrounding, these deliveries offer timely visibility of recent changes, supporting rapid assessment of construction progress and evolving site conditions.


Earth Observation delivers tangible benefits across all actors involved in large infrastructure projects:
- For construction companies. Improved visibility of project progress, support for coordination, and objective documentation of construction phases.
- For public authorities. Independent monitoring, transparent reporting, and scalable oversight of complex urban works
- For urban planners and citizens. Clear visual evidence of how projects evolve, helping communicate impact, disruption, and long-term benefits.
From Construction to Final Analysis
Monitoring does not end once the excavation is complete. Continued Earth Observation allows the project to be tracked through later construction stages and into its final configuration. Once traffic is fully relocated underground, satellite imagery will enable a post-construction analysis, documenting the recovery of surface space and the emergence of new urban uses.
The A-5 undergrounding illustrates how large-scale infrastructure can transform the relationship between mobility and urban space. Earth Observation plays a key role in this process, providing objective, timely, and scalable insights throughout the project lifecycle.
As construction continues, we will maintain monitoring and share a final analysis once the project is completed, offering a comprehensive view of Madrid’s transition from highway to future green corridor.
Thanks to our own satellites, together with our partners, we deliver high quality imagery and analytics for high impact insights which result in improved decision making.





